Lost Springs, Kansas
Lost Springs, Kansas | |
|---|---|
 Location within Marion County and Kansas | |
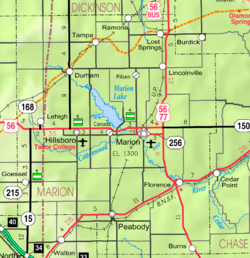 | |
| Coordinates: 38°34′00″N 96°57′57″W / 38.56667°N 96.96583°W[1] | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Kansas |
| County | Marion |
| Township | Lost Springs |
| Platted | 1887 |
| Incorporated | 1904 |
| Named for | Nearby mineral spring |
| Government | |
| • Type | Mayor–Council |
| Area | |
• Total | 0.22 sq mi (0.57 km2) |
| • Land | 0.22 sq mi (0.57 km2) |
| • Water | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km2) |
| Elevation | 1,490 ft (450 m) |
| Population | |
• Total | 55 |
| • Density | 250/sq mi (96/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC-6 (CST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-5 (CDT) |
| ZIP code | 66859 |
| Area code | 785 |
| FIPS code | 20-42825 |
| GNIS ID | 2395768[1] |
Lost Springs is a city in Marion County, Kansas, United States.[1] As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 55.[3] The city was named for a nearby lost spring that was a camping spot along the 19th century Santa Fe Trail.[4] It is located south of Herington, about 0.6 miles west of the intersection of U.S. Route 77 (aka U.S. Route 56) highway and 340th Street next to the Union Pacific Railroad.
History
[edit]Early history
[edit]For many millennia, the Great Plains of North America was inhabited by nomadic Native Americans. From the 16th century to 18th century, the Kingdom of France claimed ownership of large parts of North America. In 1762, after the French and Indian War, France secretly ceded New France to Spain, per the Treaty of Fontainebleau.
19th century
[edit]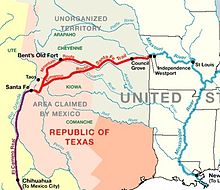
In 1802, Spain returned most of the land to France. In 1803, most of the land for modern day Kansas was acquired by the United States from France as part of the 828,000 square mile Louisiana Purchase for 2.83 cents per acre.
From the 1820s to the 1870s, one of the most significant land routes in the United States was the Santa Fe Trail. The "Lost Spring" was one of the favorite camping spots on the Santa Fe Trail because it generally had an ample supply of good water. It was located 15 miles west of Diamond Spring, which was a day's travel for a wagon train. The spring apparently got its name because it is a periodic spring, drying up at times for a week, a month, or even two years, so those visiting the site sometimes could not locate the spring on a return trip. A stage station was set up nearby in 1859 and was known as the Lost Springs Station, but no visible evidence remains of the station.[5] The trail was active across Marion County from 1821 to 1866.[6]
In 1854, the Kansas Territory was organized, then in 1861 Kansas became the 34th U.S. state. In 1855, Marion County was established within the Kansas Territory, which included the land for modern day Lost Springs.[7]

A post office existed in Lost Spring from August 29, 1861, to May 23, 1864. Later, the post office was reestablished as Lost Springs on July 9, 1879.[8]
In 1887, the Chicago, Kansas and Nebraska Railway built a branch line north–south from Herington through Lost Springs to Caldwell.[9] It foreclosed in 1891 and was taken over by Chicago, Rock Island and Pacific Railway, which shut down in 1980 and reorganized as Oklahoma, Kansas and Texas Railroad, merged in 1988 with Missouri Pacific Railroad, and finally merged in 1997 with Union Pacific Railroad. Most locals still refer to this railroad as the "Rock Island".

In 1887, Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway built a branch line from Neva (3 miles west of Strong City) to Superior, Nebraska. This branch line connects Strong City, Neva, Rockland, Diamond Springs, Burdick, Lost Springs, Jacobs, Hope, Navarre, Enterprise, Abilene, Talmage, Manchester, Longford, Oak Hill, Miltonvale, Aurora, Huscher, Concordia, Kackley, Courtland, Webber, Superior. In 1996, the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway merged with Burlington Northern Railroad and renamed to the current BNSF Railway. Most locals still refer to this railroad as the "Santa Fe".
At some point, the "Santa Fe" line from Neva to Lost Springs was pulled but the right of way has not been abandoned. This branch line was originally called "Strong City and Superior line" but later the name was shortened to the "Strong City line". The two railways are connected via a switch to allow north-bound "Rock Island" traffic to connect onto the north-west-bound "Santa Fe" tracks. This is the only way for the Santa Fe traffic to travel north-west after removing the tracks to Neva.
20th century
[edit]The National Old Trails Road, also known as the Ocean-to-Ocean Highway, was established in 1912, and was routed through Lehigh, Hillsboro, Marion, Lost Springs.
Geography
[edit]Lost Springs is located in the scenic Flint Hills and Great Plains of the state of Kansas.[1] According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 0.23 square miles (0.60 km2), all of it land.[10] The county line is 1.7 miles east of Lost Springs.
Climate
[edit]The climate in this area is characterized by hot, humid summers and generally mild to cool winters. According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, Lost Springs has a humid subtropical climate, abbreviated "Cfa" on climate maps.[11]
Demographics
[edit]| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1910 | 276 | — | |
| 1920 | 261 | −5.4% | |
| 1930 | 265 | 1.5% | |
| 1940 | 255 | −3.8% | |
| 1950 | 184 | −27.8% | |
| 1960 | 139 | −24.5% | |
| 1970 | 103 | −25.9% | |
| 1980 | 94 | −8.7% | |
| 1990 | 106 | 12.8% | |
| 2000 | 71 | −33.0% | |
| 2010 | 70 | −1.4% | |
| 2020 | 55 | −21.4% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census | |||
2020 census
[edit]The 2020 United States census counted 55 people, 27 households, and 19 families in Lost Springs.[12][13] The population density was 247.7 per square mile (95.7/km2). There were 29 housing units at an average density of 130.6 per square mile (50.4/km2).[13][14] The racial makeup was 96.36% (53) white or European American (92.73% non-Hispanic white), 0.0% (0) black or African-American, 0.0% (0) Native American or Alaska Native, 0.0% (0) Asian, 0.0% (0) Pacific Islander or Native Hawaiian, 0.0% (0) from other races, and 3.64% (2) from two or more races.[15] Hispanic or Latino of any race was 7.27% (4) of the population.[16]
Of the 27 households, 29.6% had children under the age of 18; 51.9% were married couples living together; 25.9% had a female householder with no spouse or partner present. 25.9% of households consisted of individuals and 11.1% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older.[13] The average household size was 2.8 and the average family size was 2.9.[17] The percent of those with a bachelor’s degree or higher was estimated to be 9.1% of the population.[18]
23.6% of the population was under the age of 18, 9.1% from 18 to 24, 20.0% from 25 to 44, 25.5% from 45 to 64, and 21.8% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 40.6 years. For every 100 females, there were 111.5 males.[13] For every 100 females ages 18 and older, there were 82.6 males.[13]
The 2016-2020 5-year American Community Survey estimates show that the median household income was $52,250 (with a margin of error of +/- $19,147) and the median family income was $61,000 (+/- $22,498).[19] Males had a median income of $26,563 (+/- $836). The median income for those above 16 years old was $26,458 (+/- $4,659).[20] Approximately, 12.5% of families and 20.0% of the population were below the poverty line, including 33.3% of those under the age of 18 and 17.6% of those ages 65 or over.[21][22]
2010 census
[edit]As of the census[23] of 2010, there were 70 people, 26 households, and 23 families residing in the city. The population density was 304.3 inhabitants per square mile (117.5/km2). There were 30 housing units at an average density of 130.4 per square mile (50.3/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 82.9% White, 1.4% Native American, 7.1% from other races, and 8.6% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 14.3% of the population.
There were 26 households, of which 26.9% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 61.5% were married couples living together, 11.5% had a female householder with no husband present, 15.4% had a male householder with no wife present, and 11.5% were non-families. 11.5% of all households were made up of individuals. The average household size was 2.69 and the average family size was 2.70.
The median age in the city was 45.5 years. 18.6% of residents were under the age of 18; 11.4% were between the ages of 18 and 24; 20% were from 25 to 44; 27.2% were from 45 to 64; and 22.9% were 65 years of age or older. The gender makeup of the city was 55.7% male and 44.3% female.
2000 census
[edit]As of the census[24] of 2000, there were 71 people, 30 households, and 23 families residing in the city. The population density was 308.3 inhabitants per square mile (119.0/km2). There were 34 housing units at an average density of 147.6 per square mile (57.0/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 92.96% White, 1.41% Native American, 2.82% from other races, and 2.82% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 7.04% of the population.
There were 30 households, out of which 36.7% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 56.7% were married couples living together, 16.7% had a female householder with no husband present, and 23.3% were non-families. 23.3% of all households were made up of individuals, and 13.3% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.37 and the average family size was 2.70.
In the city, the population was spread out, with 28.2% under the age of 18, 5.6% from 18 to 24, 25.4% from 25 to 44, 28.2% from 45 to 64, and 12.7% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 39 years. For every 100 females, there were 91.9 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 82.1 males.
As of 2000 the median income for a household in the city was $15,455, and the median income for a family was $16,250. Males had a median income of $15,625 versus $11,250 for females. The per capita income for the city was $7,227. There were 15.8% of families and 21.7% of the population living below the poverty line, including 29.4% of under eighteens and none of those over 64.
Area attractions
[edit]
Lost Springs has one listing on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP).
- Santa Fe Trail
- Lost Spring[5] (NRHP), 2.5 mi west of Lost Springs on 340th Street. From the 1820s to the 1870s, one of the most significant land routes in the United States was the Santa Fe Trail, and ran south of the spring.[25] Lost Spring was one of the favorite camping spots on the Santa Fe Trail because it generally had an ample supply of good water.
- Santa Fe Trail Markers, numerous markers in the area.[26][27][28]
- Santa Fe Trail Self-Guided Auto Tour.
Government
[edit]The Lost Springs government consists of a mayor and five council members. The council meets the 2nd Wednesday of each month at 7PM.[29]
- City Hall.
- Fire Department.
- U.S. Post Office, 125 Berry St.
Education
[edit]The community is served by Centre USD 397 public school district. The high school is a member of T.E.E.N., a shared video teaching network between five area high schools.[30]
- Centre School; 2374 310th St, Lost Springs, KS; between Lost Springs and Lincolnville, east of U.S. 77 highway.
- Sports
The Centre High School mascot is a Cougar. All high school athletic and non-athletic competition is overseen by the Kansas State High School Activities Association. For 2010/2011 seasons, the football team competes as Class 8 Man - Division II.[31]
Media
[edit]- Marion County Record, county newspaper for Marion County.
- Hillsboro Free Press, free newspaper for greater Marion County area.
- The Herington Times, newspaper from Herington.
Infrastructure
[edit]
Transportation
[edit]Highway U.S. Route 77 is 0.8 mi east of Lost Springs. Lost Springs is served by the Union Pacific Railroad, formerly the Oklahoma, Kansas and Texas Railroad, and prior, the Chicago, Rock Island and Pacific Railroad. Lost Springs is located on UP's Texas main line to Fort Worth, Texas. A rail siding is located there for meets with passing trains, before entering UP's Herington, Kansas yard. The Burlington Northern Santa Fe Railway, formerly the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway, also has a line that enters the area, and connects with the UP at the Northeast corner of town. At one time this line crossed over the UP at a diamond crossing, and continued east towards Burdick, Kansas, but it has since been removed.
Utilities
[edit]- Internet
- TV
- Fiber Optics is provided by TCT.
- Satellite is provided by DirecTV, Dish Network.
- Terrestrial is provided by regional digital TV stations.
- Telephone
- Fiber Optics is provided by TCT.
- Electricity
- Rural is provided by Flint Hills RECA.
Notable people
[edit]- Lloyd Metzler, (1913–1980), American economist.
- William R. Novak, (1929–2012), Kansas House of Representatives, Farmer, Stockman, Wholesale Aircraft Parts. Appointed February 29, 1972, to replace Lawrence D. Slocombe (Peabody) who died while in office.[32]
See also
[edit]- Centre High School
- National Register of Historic Places listings in Marion County, Kansas
- Historical Maps of Marion County, Kansas
- Santa Fe Trail
- National Old Trails Road
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Lost Springs, Kansas
- ^ "2019 U.S. Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 24, 2020.
- ^ a b "Profile of Lost Springs, Kansas in 2020". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on November 11, 2021. Retrieved November 11, 2021.
- ^ Marion County Kansas, Past and Present; Sondra Van Meter; 1972.
- ^ a b National Register of Historic Places - Lost Spring
- ^ History of the Cottonwood Crossing Chapter, Santa Fe Trail Association.
- ^ The History of Marion County and Courthouse
- ^ "Kansas Post Offices, 1828-1961 (archived)". Kansas Historical Society. Archived from the original on October 9, 2013. Retrieved June 14, 2014.
- ^ "Rock Island Rail History". Archived from the original on June 19, 2011. Retrieved July 31, 2010.
- ^ "US Gazetteer files 2010". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on July 2, 2012. Retrieved July 6, 2012.
- ^ Climate Summary for Lost Springs, Kansas
- ^ "US Census Bureau, Table P16: HOUSEHOLD TYPE". data.census.gov. Retrieved January 3, 2024.
- ^ a b c d e "US Census Bureau, Table DP1: PROFILE OF GENERAL POPULATION AND HOUSING CHARACTERISTICS". data.census.gov. Retrieved January 3, 2024.
- ^ Bureau, US Census. "Gazetteer Files". Census.gov. Retrieved December 30, 2023.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ "US Census Bureau, Table P1: RACE". data.census.gov. Retrieved January 3, 2024.
- ^ "US Census Bureau, Table P2: HISPANIC OR LATINO, AND NOT HISPANIC OR LATINO BY RACE". data.census.gov. Retrieved January 3, 2024.
- ^ "US Census Bureau, Table S1101: HOUSEHOLDS AND FAMILIES". data.census.gov. Retrieved January 3, 2024.
- ^ "US Census Bureau, Table S1501: EDUCATIONAL ATTAINMENT". data.census.gov. Retrieved January 3, 2024.
- ^ "US Census Bureau, Table S1903: MEDIAN INCOME IN THE PAST 12 MONTHS (IN 2020 INFLATION-ADJUSTED DOLLARS)". data.census.gov. Retrieved January 3, 2024.
- ^ "US Census Bureau, Table S2001: EARNINGS IN THE PAST 12 MONTHS (IN 2020 INFLATION-ADJUSTED DOLLARS)". data.census.gov. Retrieved January 3, 2024.
- ^ "US Census Bureau, Table S1701: POVERTY STATUS IN THE PAST 12 MONTHS". data.census.gov. Retrieved January 3, 2024.
- ^ "US Census Bureau, Table S1702: POVERTY STATUS IN THE PAST 12 MONTHS OF FAMILIES". data.census.gov. Retrieved January 3, 2024.
- ^ "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 6, 2012.
- ^ "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- ^ Santa Fe Trail map
- ^ Santa Fe Trail Historical Marker 1
- ^ Santa Fe Trail Historical Marker 2
- ^ Lost Spring Marker Moving Day
- ^ Lost Springs - Directory of Public Officials
- ^ T.E.E.N. video teaching network
- ^ KSHSAA Football Class Size Assignments Archived 2010-09-23 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Kansas Legislators Past & Present Archived 2010-08-01 at the Wayback Machine
Further reading
[edit]- Early Settlement of Lost Springs; Marion Review; September 15, 1937.
External links
[edit]- City
- Lost Springs - Directory of Public Officials, League of Kansas Municipalities
- Historical
- Historic Images of Lost Springs, Special Photo Collections at Wichita State University Library.
- Marion County cemetery list, archive of KsGenWeb
- Marion County history bibliography, Marion County school bibliography, Kansas Historical Society
- Lost Springs - Santa Fe Trail Research site
- Maps

